How To Turn On Pi Camera
Getting Started with Raspberry Pi Camera¶
In this tutorial we volition go through how to ready up the Raspberry Pi Camera. We will become through the installation, enabling camera from the Pi, testing the photographic camera, and writing Python code for taking individual pictures. We will also cover how to set up Node-RED to easily take pictures with the PiCamera or command the camera remotely the PiCamera remotely.
Hardware installation¶
Starting time, observe the camera port on the Raspberry Pi iii. It is located right adjacent to the HDMI port. Gently lift the white collar on the port. Adjacent, insert the cable into the camera port, the side with blue texts facing the Ethernet port. Make sure that the cable is inserted all the way in. Gently push down the white neckband to secure the cable.
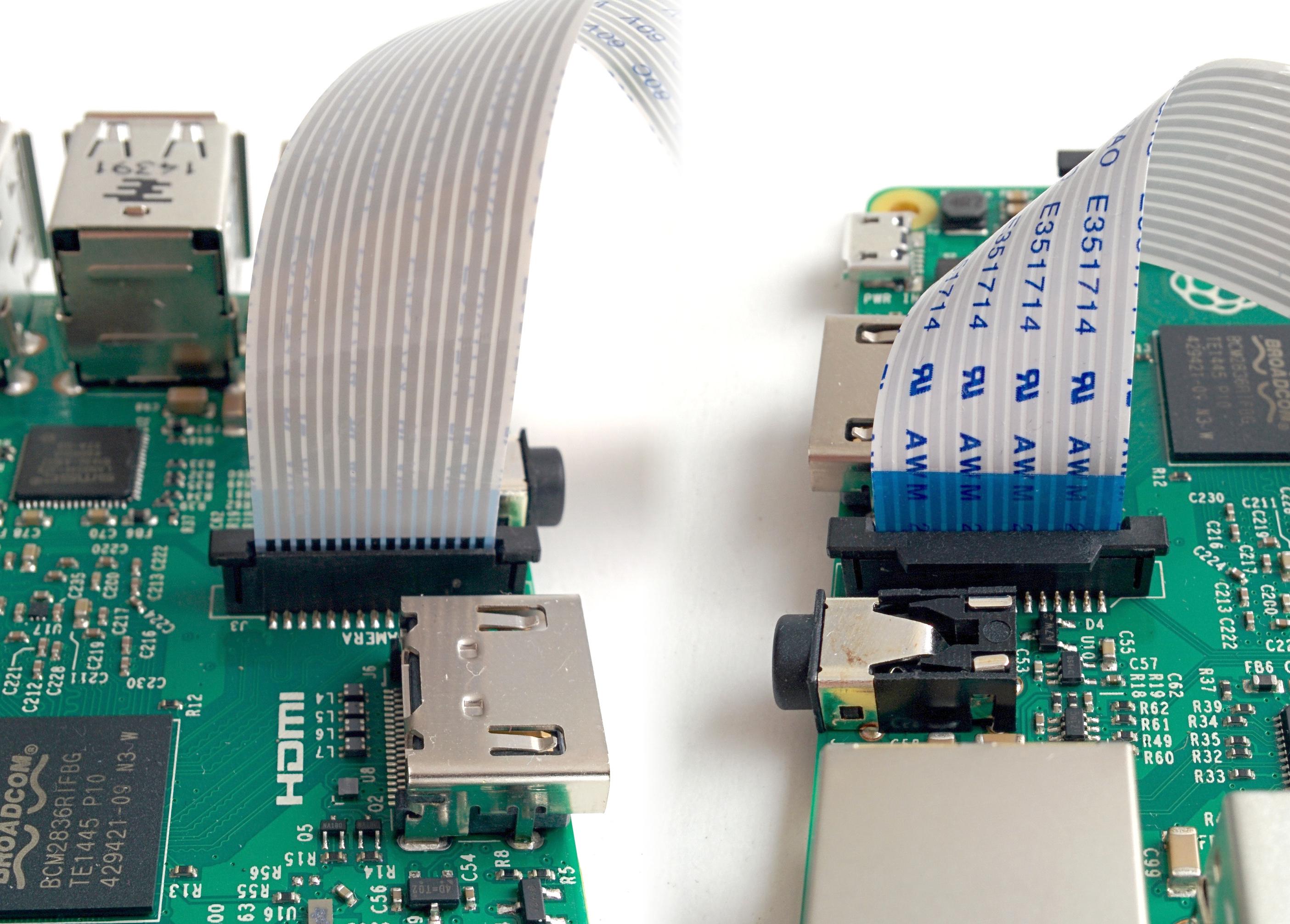
Note
If you also need to accept a SenseHAT installed, make certain that yous stick the cable through the slot on the SenseHAT first. Otherwise it will be difficult to install the PiCamera later you install SenseHAT.
Software setup¶
The camera interface on the Raspberry Pi is not turned on past default. You will demand to manually turn it on. In that location are two means to do this:
- Through the raspi-config utility
- Through the Raspberry Pi settings on the desktop.
Turning on the camera interface through raspi-config¶
Type the following control in the terminal (located on the task bar, or printing Ctrl+Alt+T):
In the terminal interface that follows, choose Interfacing Options, and then Photographic camera. Choose yep, salvage the configuration, and reboot the Raspberry Pi.
Turning on the camera interface through the GUI¶
Start the Raspberry Pi Configuration utility and enable the camera module:
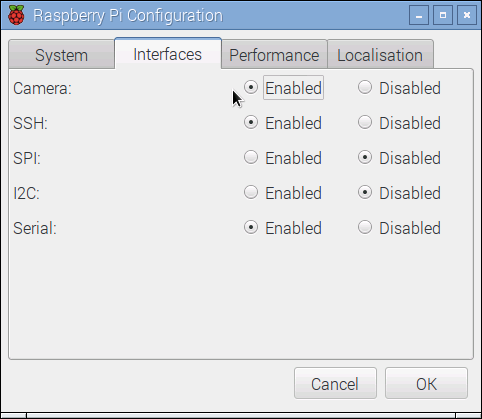
You will likewise need to reboot your Raspberry Pi afterward this.
Test your configuration¶
To make certain that your Camera is fix properly, use this command:
$ raspistill -o image.jpg A preview of the photographic camera should appear, and later on 5 seconds, you will see an image chosen image.jpg in the homepi folder.
Hint
If you are using VNC, yous will need to go to settings of the VNC client on the Raspberry Pi. Navigate to Menu > Options > Troubleshooting and select Enable experimental direct capture mode.
Next, make sure that yous have the Python library installed. In the last, type this:
$ python3 -c "import picamera" If no mistake letters pop up, congratulations. You've configured your Raspberry Pi correctly.
Programming your PiCamera¶
Warning
When trying out these scripts do non name your file picamera.py . Naming scripts after existing Python modules will cause errors when you attempt and import those modules (considering Python checks the current directory earlier checking other paths).
Starting a preview¶
from picamera import PiCamera camera = PiCamera () photographic camera . resolution ( 1024 , 768 ) # 4:3 attribute ratio photographic camera . start_preview () Yous will demand the first two lines before you lot instruct the PiCamera to do annihilation. The thrid line sets up the resolution for the camera. The camera supports taking 4K videos at 30FPS!
Taking a picture¶
from time import sleep from picamera import PiCamera camera = PiCamera () camera . resolution = ( 1600 , 1200 ) # iv:three aspect ratio sleep ( 2 ) # warming upward camera . capture ( 'foo.jpg' ) Capturing timelapse sequences¶
The simplest way to capture long time-lapse sequences is with the capture_continuous() method. With this method, the camera captures images continually until y'all tell it to stop. Images are automatically given unique names and you can easily control the delay between captures. The following example shows how to capture images with a five minute delay betwixt each shot::
from time import sleep from picamera import PiCamera camera = PiCamera () photographic camera . start_preview () slumber ( two ) for filename in camera . capture_continuous ( 'img {counter:03d} .jpg' ): print ( 'Captured %due south ' % filename ) sleep ( 300 ) # wait 5 minutes Nevertheless, you may wish to capture images at a particular time, say at the start of every 60 minutes. This merely requires a refinement of the delay in the loop (the datetime module is slightly easier to utilize for calculating dates and times; this instance too demonstrates the timestamp template in the captured filenames)::
from time import slumber from picamera import PiCamera from datetime import datetime , timedelta def wait (): # Calculate the delay to the start of the next hour next_hour = ( datetime . now () + timedelta ( 60 minutes = 1 )) . replace ( minute = 0 , second = 0 , microsecond = 0 ) delay = ( next_hour - datetime . now ()) . seconds sleep ( delay ) camera = PiCamera () camera . start_preview () await () for filename in camera . capture_continuous ( 'img{timestamp:%Y-%thou- %d -%H-%M}.jpg' ): print ( 'Captured %south ' % filename ) await () Controlling the PiCamera using Node-RED¶
Node-RED offers a myriad of functionalities to control the Raspberry Pi. The only thing you demand to do is to install the camerapi node:
$ cd .node-cerise $ npm install node-reddish-contrib-camerapi Once the camerapi node is installed, kickoff Node-RED by going to the Programming menu, click on Node-RED. Get out the terminal window open, fire up a new browser window, and get to http://127.0.0.1:1880. You will need an inject node, and a camerapi takephoto node. Drag them to an empty flow, and connect them. Double-click on the camera pi node, you volition see the following setting:

The but option that needs explanation is the first one. The File Mode option controls how the files are named. Choose Generate and the file proper noun will be generated automatically. Choose Filemode, y'all can specify the file name. You lot can also cull to override the file name using msg.filename in the msg object passed to the node, and so that you can write a function to fine command the filename.
Annotation
Yous tin can find your picture show under the /home/pi/Pictures binder.
Now y'all tin deploy the period. Whenever you lot click the button to the left of the inject node, a new pic will be taken.
Alternatively, you can also change the options of the inject node to take Node-RED take the pic at a sure time interval by changing the echo option.

Source: http://nodepy-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/picamera-start.html
Posted by: leonreaccurtut.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Turn On Pi Camera"
Post a Comment